TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Requirements & Design
4. Implementation
5. Result and Evaluation
6. Conclusion
7. References
8. Source Code
1. Introduction
Contact Management System is a simple console application that is developed in C Language. This program enables to store data and manage contact information. Those are essentially databases that track all (i.e. Name, Phone Number and Email address) information and communication based on user contacts.
2. Background
Features for this application: Login, Show Contact List, Insert/Add Contact, Delete Contact, Search Contact, Security Settings, Change Username and Password, Sort Contact, Log Out, Login Again or Exit program. For this project, all of the contents based on C Language.
3. Requirements & Design
Contact Management System is console base project without graphics. It is similar to the contact manager in cell phones. This mini project use file handling and data structures. For design this project I used array, function, if...else, for loop, nested loop, switch, case, and etc. Basically, this is an easy and fundamental level mini project for learning purposes. We used simple design for this project.
4. Implementation
Describe the program code in below for understanding this project-
4.1 Set Username and Password
If user run this project for first time, Set Username and Password is mandatory option to manage contact. After set Username and Password, this is not required for next time.
Sample output: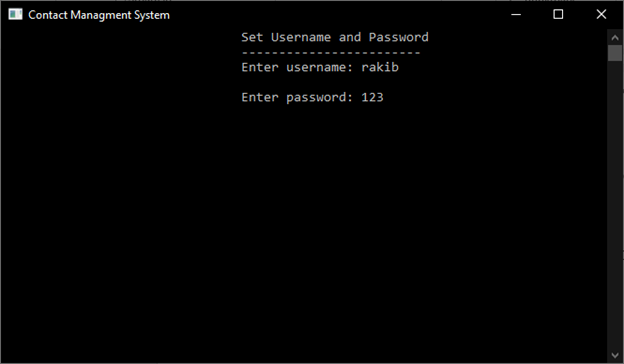
4.2 Login to manage contacts
After set Username and Password, Login to manage contacts is another mandatory option to manage contacts.
Sample output: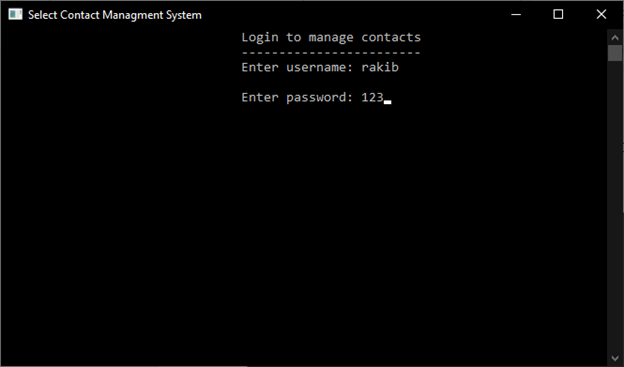
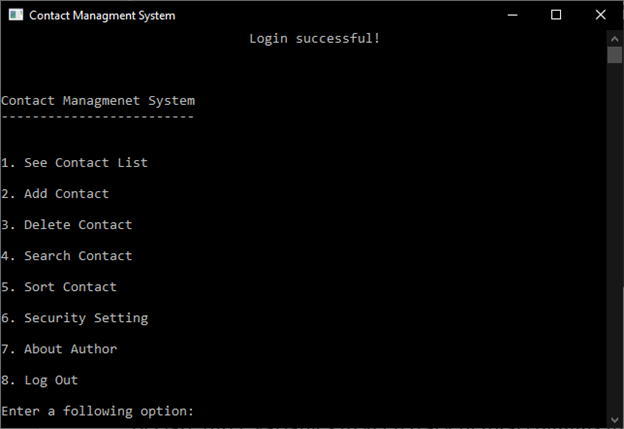
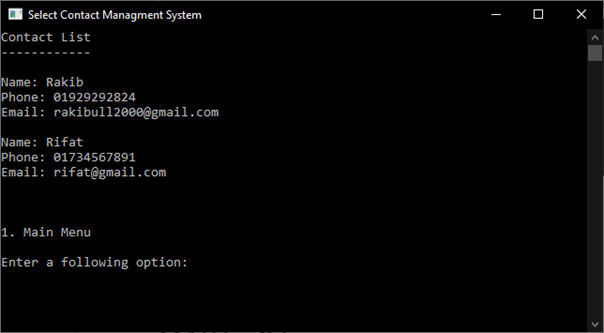
4.3.1 See Contact List
See Contact List can help to show all contact.
Sample output:
4.4.2 Add Contact
Add Contact can add Name, Phone Number and Email Address in Contact list.
Sample output: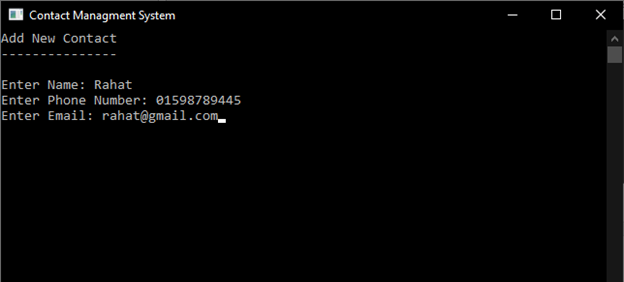
4.5.3 Delete Contact
Delete Contact can delete Name, Phone Number and Email Address in Contact list on specific position.
Sample output: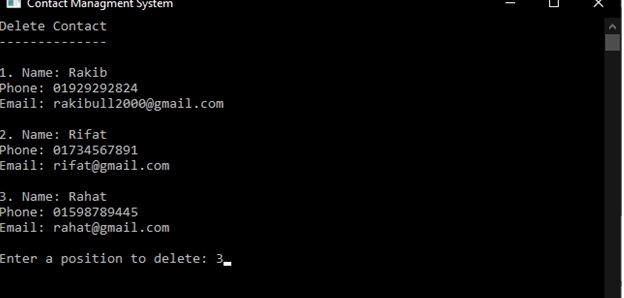
4.5.4 Search Contact
Search Contact can search by Name or Phone Number in Contact list for easily find people.
Sample Output: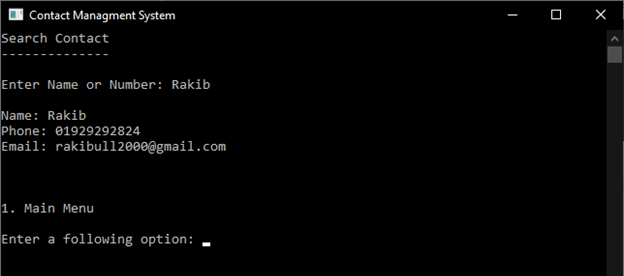
4.5.5 Sort Contact
Sort Contact can sort by Name or Phone Number on Contact list.
Sample Output: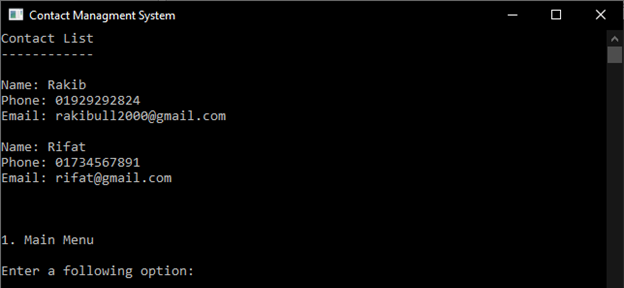
4.5.6 Security Setting
For this project, the user can change Username and Password by Security Setting.
Sample Output:
4.5.8 Log Out
The user can log out from all features by Log Out option.
Sample Output:
5. Result and Evaluation
After run this project, we can see many features and add Name, Phone Number and Email address as Contact Management System. Here, the data will be stored in the ContactList.txt file. If the file is deleted, the user must lost his/her all data.
6. Conclusion
The principle behind constructing a Contact Management System is to effectively retrieve and implement any information. All the information related to a particular people can be linked and archived only to be retrieved later when they are required most.
7. References
This project based on Data Structure.
Source Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
int size = 0, i = 0, j, position, option, isFound = 0, m, n;
FILE *fp;
char search[20];
struct contact
{
char name[20], phone[20], email[30], username[20], password[20];
} list[100], temp;
int fileOpenRead();
int fileOpenWrite();
int readFile();
int mainMenu();
int main();
int forgetUserPass();
int optionMenu()
{
printf("\n\n1. Main Menu\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
mainMenu();
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input for Main Menu!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
}
int aboutAuthor()
{
printf("Rakibul Islam\n\n");
optionMenu();
system("cls");
}
int contactList()
{
printf("Contact List");
printf("\n------------\n\n");
fileOpenRead();
for(j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
printf("Name: %s\nPhone: %s\nEmail: %s\n\n", list[j].name, list[j].phone, list[j].email);
}
fclose(fp);
optionMenu();
}
int optionMenuTwo()
{
printf("\n\n1. Contact List\n2. Main Menu\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
contactList();
break;
case 2:
mainMenu();
default:
printf("Invalid Input for Main Menu!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
}
int addContact()
{
readFile();
printf("Add New Contact");
printf("\n---------------\n\n");
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
printf("Enter Name: ");
scanf("%s", list[i].name);
printf("Enter Phone Number: ");
scanf("%s", list[i].phone);
printf("Enter Email: ");
scanf("%s", list[i].email);
size++;
i++;
fileOpenWrite();
readFile();
printf("\n\n1. Contact List\n2. Add New Contact\n3. Main Menu\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
printf("\n");
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
contactList();
break;
case 2:
addContact();
break;
case 3:
mainMenu();
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input for Main Menu!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
}
int deleteContact()
{
printf("Delete Contact");
printf("\n--------------\n\n");
readFile();
fileOpenRead();
for(j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
printf("%d. Name: %s\nPhone: %s\nEmail: %s\n\n", j + 1, list[j].name, list[j].phone, list[j].email);
}
fclose(fp);
printf("Enter a position to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &position);
if(position <= j && position > 0)
{
fileOpenRead();
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
for(j = position; j < size; j++)
{
strcpy(list[j - 1].name, list[j].name);
strcpy(list[j - 1].phone, list[j].phone);
strcpy(list[j - 1].email, list[j].email);
}
size--;
i--;
j--;
fileOpenWrite();
readFile();
system("cls");
printf("Deleted!");
optionMenuTwo();
}
else
{
system("cls");
printf("Invalid Position!");
optionMenu();
}
}
int searchContact()
{
printf("Search Contact");
printf("\n--------------\n\n");
fileOpenRead();
printf("Enter Name or Number: ");
scanf("%s", search);
printf("\n");
for(j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
if((strcmp(search, list[j].name) == 0))
{
printf("Name: %s\nPhone: %s\nEmail: %s\n\n", list[j].name, list[j].phone, list[j].email);
isFound = 1;
}
else if((strcmp(search, list[j].phone) == 0))
{
printf("Name: %s\nPhone: %s\nEmail: %s\n\n", list[j].name, list[j].phone, list[j].email);
isFound = 1;
}
}
fclose(fp);
if(isFound == 1);
else
{
printf("Not Found!\n\n");
}
optionMenu();
}
int SortByName()
{
fileOpenRead();
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
for(m = 0; m < size - 1; m++)
{
for(n = 0; n < size - m - 1; n++)
{
if(strcmp(list[n].name, list[n + 1].name) > 0)
{
temp = list[n];
list[n] = list[n + 1];
list[n + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
fileOpenWrite();
readFile();
printf("Sorted!");
optionMenuTwo();
}
int SortByNumber()
{
fileOpenRead();
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
for(m = 0; m < size - 1; m++)
{
for(n = 0; n < size - m - 1; n++)
{
if(strcmp(list[n].phone, list[n + 1].phone) > 0)
{
temp = list[n];
list[n] = list[n + 1];
list[n + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
fileOpenWrite();
readFile();
printf("Sorted!");
optionMenuTwo();
}
int SortContact()
{
printf("Sort Contact");
printf("\n--------------\n\n");
readFile();
printf("1. Sort by Name\n2. Sort by Number\n3. Main Menu\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
SortByName();
break;
case 2:
SortByNumber();
break;
case 3:
mainMenu();
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input for Main Menu!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
}
int changeUsername()
{
readFile();
printf("Change Username");
printf("\n------------\n\n");
fileOpenRead();
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
printf("New Username: ");
scanf("%s", list[1].username);
printf("Password: ");
scanf("%s", list[1].password);
if(strcmp(list[1].password, list[0].password) == 0)
{
system("cls");
strcpy(list[0].username, list[1].username);
printf("Username changed successfully!");
printf("\n\n");
fileOpenWrite();
fclose(fp);
readFile();
optionMenu();
}
else
{
fclose(fp);
system("cls");
printf("Wrong password!\n\n");
forgetUserPass();
}
}
int changePassword()
{
readFile();
printf("Change Password");
printf("\n---------------\n\n");
fileOpenRead();
printf("Password: ");
scanf("%s", list[1].password);
if(strcmp(list[1].password, list[0].password) == 0)
{
printf("New Password: ");
scanf("%s", list[2].password);
confirmNewPass:
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
printf("Confirm New Password: ");
scanf("%s", list[3].password);
if(strcmp(list[2].password, list[3].password) == 0)
{
strcpy(list[0].password, list[3].password);
fileOpenWrite();
fclose(fp);
system("cls");
printf("Password changed successfully!");
printf("\n\n");
readFile();
optionMenu();
}
else
{
system("cls");
printf("New Password and Confirm New Password are not same!");
printf("\n\n");
//printf("Password: %s\nNew Password: %s\n", list[1].password, list[2].password);
printf("New Password: %s\n", list[2].password);
goto confirmNewPass;
}
}
else
{
fclose(fp);
readFile();
system("cls");
printf("Wrong password!\n\n");
forgetUserPass();
}
}
int securitySetting()
{
printf("Security Setting");
printf("\n-------------------\n\n");
printf("\n\n1. Change Username\n2. Change Password\n3. Main Menu\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
changeUsername();
break;
case 2:
changePassword();
break;
case 3:
mainMenu();
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input for Main Menu!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
readFile();
}
int LoggedOutPage()
{
printf("Logged Out!\n\n");
loginOption:
printf("1. Login\n2. Exit\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
main();
break;
case 2:
printf("Exiting...\n\n");
exit(0);
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input!\n\n");
goto loginOption;
break;
}
}
int forgetUserPass()
{
printf("Forget Username or Passwowrd");
printf("\n---------------------------\n\n");
printf("\n\n1. Show Username\n2. Show Password\n3. Main Menu\n\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
printf("Username: %s", list[0].username);
optionMenu();
break;
case 2:
printf("Password: %s", list[0].password);
optionMenu();
break;
case 3:
mainMenu();
break;
default:
system("cls");
printf("Invalid Input!\n\n");
mainMenu();
break;
}
}
int mainMenu()
{
printf("Contact Managmenet System");
printf("\n-------------------------\n\n\n");
printf("1. See Contact List\n\n");
printf("2. Add Contact\n\n");
printf("3. Delete Contact\n\n");
printf("4. Search Contact\n\n");
printf("5. Sort Contact\n\n");
printf("6. Security Setting\n\n");
printf("7. About Author\n\n");
printf("8. Log Out\n\n");
printf("Enter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
printf("\n");
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
contactList();
break;
case 2:
addContact();
break;
case 3:
deleteContact();
break;
case 4:
searchContact();
break;
case 5:
SortContact();
break;
case 6:
securitySetting();
break;
case 7:
aboutAuthor();
break;
case 8:
LoggedOutPage();
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input! Please Enter 1 to 6:\n\n");
break;
}
}
int main()
{
SetConsoleTitle("Contact Managment System");
//Default Password and Username.
//strcpy(list[0].username, "0");
//strcpy(list[0].password, "0");
readFile();
fileOpenRead();
if(strcmp(list[0].username, "") == 0 && strcmp(list[0].password, "") == 0)
{
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "wb");
printf("\t\t\t\tSet Username and Password\n");
printf("\t\t\t\t------------------------\n");
printf("\t\t\t\tEnter username: ");
scanf("%s", list[0].username);
printf("\n\t\t\t\tEnter password: ");
scanf("%s", list[0].password);
printf("\n");
fileOpenWrite();
readFile();
fclose(fp);
system("cls");
}
fclose(fp);
login:
readFile();
fileOpenRead();
printf("\t\t\t\tLogin to manage contacts\n");
printf("\t\t\t\t------------------------\n");
printf("\t\t\t\tEnter username: ");
scanf("%s", list[1].username);
printf("\n");
printf("\t\t\t\tEnter password: ");
scanf("%s", list[1].password);
printf("\n");
if(strcmp(list[1].username, list[0].username) == 0 && strcmp(list[1].password, list[0].password) == 0)
{
fclose(fp);
system("cls");
printf("\t\t\t\tLogin successful!\n\n");
printf("\n\n");
readFile();
while(1) //1 for infinite loop.
{
mainMenu();
}
}
else
{
invalid:
system("cls");
printf("Wrong useraname or password!\n\n");
printf("1. Forget Useraname or Password\n2. Login\n\nEnter a following option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
system("cls");
switch(option)
{
case 1:
printf("After few second it's automatically go Login page.\n\n");
printf("Username: %s\nPassword: %s\n\nPlease wait...", list[0].username, list[0].password);
Sleep(5000);
system("cls");
goto login;
break;
case 2:
goto login;
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Input!\n\n");
goto invalid;
break;
}
}
}
int fileOpenRead()
{
fp = fopen("ContactList.txt", "rb");
fread(&list, sizeof(list), 1, fp);
fread(&size, sizeof(size), 1, fp);
fread(&i, sizeof(i), 1, fp);
}
int fileOpenWrite()
{
fwrite(&list, sizeof(list), 1, fp);
fwrite(&size, sizeof(size), 1, fp);
fwrite(&i, sizeof(i), 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
}
int readFile()
{
fileOpenRead();
for(j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
list[j].name;
list[j].phone;
list[j].email;
}
fclose(fp);
}











